 If you’ve made the choice to replace your missing teeth with dental implants, you’ve made a smart decision. We provide dental implants in Beachwood to allow you to make an investment in your smile with a permanent solution to treat tooth loss. Using a simple and safe surgical procedure, you’ll benefit from permanent prosthetic teeth to regain your smile, oral health and quality of life. While dental implants are highly successful, we understand you may still have some questions about the procedure. As your implant dentist in Beachwood, we’re here to help you understand to process to getting dental implants.
If you’ve made the choice to replace your missing teeth with dental implants, you’ve made a smart decision. We provide dental implants in Beachwood to allow you to make an investment in your smile with a permanent solution to treat tooth loss. Using a simple and safe surgical procedure, you’ll benefit from permanent prosthetic teeth to regain your smile, oral health and quality of life. While dental implants are highly successful, we understand you may still have some questions about the procedure. As your implant dentist in Beachwood, we’re here to help you understand to process to getting dental implants.
(more…)
What to Expect When Getting Dental Implants
May 28, 2016
The Alternative Sleep Apnea Treatment Beachwood Residents Prefer
November 18, 2015
 Sleep apnea is the cessation of breathing during sleep for at least 10 seconds at a time. There are two types of sleep apnea: central and obstructive. Central sleep apnea (CSA) is a disorder that causes the brain to stop sending the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. The most common form of sleep apnea is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). This form of apnea occurs when airways are blocked during sleep causing the cessation of breathing. Many patients are treated using Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) that, as the name suggests, keeps airways open using a continual flow of air. Many CPAP users are unhappy with the system because the sounds it makes are loud, they can’t get used to the sensation of forced air, and because the CPAP system is inconvenient for travel. For patients who suffer from OSA, our Beachwood, OH dental team has an alternative to the CPAP system: oral appliance therapy with The Moses® and SomnoDent®.
Sleep apnea is the cessation of breathing during sleep for at least 10 seconds at a time. There are two types of sleep apnea: central and obstructive. Central sleep apnea (CSA) is a disorder that causes the brain to stop sending the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. The most common form of sleep apnea is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). This form of apnea occurs when airways are blocked during sleep causing the cessation of breathing. Many patients are treated using Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) that, as the name suggests, keeps airways open using a continual flow of air. Many CPAP users are unhappy with the system because the sounds it makes are loud, they can’t get used to the sensation of forced air, and because the CPAP system is inconvenient for travel. For patients who suffer from OSA, our Beachwood, OH dental team has an alternative to the CPAP system: oral appliance therapy with The Moses® and SomnoDent®.
(more…)
The Dentist Pepper Pike Prefers Says Tobacco Use Greatly Affects Oral Health
September 16, 2015
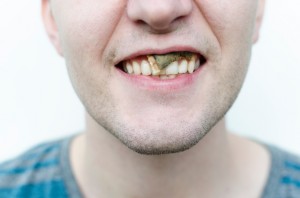 Tobacco use is rampant in the United States. Roughly 42 million people are habitual tobacco users. Of this number, many will develop conditions such as lung cancer, emphysema and more. Tobacco is enjoyed by people in several different ways including cigarettes, smokeless tobacco (“dip”), or cigars. Nicotine is highly addictive, which explains why so many people are tobacco users. We’re here to tell you that it’s in your best interest to kick the habit while you still have time. You see, it isn’t just your overall health you’re putting at risk, it’s your oral health, too. Our Beachwood, OH office wants you to know that your oral health is very important and tobacco use can leave it in bad shape. Bad oral health has a major impact on your overall health. As the Beachwood dentist of choice for residents in the area, Dr. Hornstein has firsthand the effects tobacco has had on many patients. He and the rest of our dental staff want you to live your life free of tobacco and with the best oral health of your life.
Tobacco use is rampant in the United States. Roughly 42 million people are habitual tobacco users. Of this number, many will develop conditions such as lung cancer, emphysema and more. Tobacco is enjoyed by people in several different ways including cigarettes, smokeless tobacco (“dip”), or cigars. Nicotine is highly addictive, which explains why so many people are tobacco users. We’re here to tell you that it’s in your best interest to kick the habit while you still have time. You see, it isn’t just your overall health you’re putting at risk, it’s your oral health, too. Our Beachwood, OH office wants you to know that your oral health is very important and tobacco use can leave it in bad shape. Bad oral health has a major impact on your overall health. As the Beachwood dentist of choice for residents in the area, Dr. Hornstein has firsthand the effects tobacco has had on many patients. He and the rest of our dental staff want you to live your life free of tobacco and with the best oral health of your life.
(more…)
Oral Health & Pregnancy Facts from Your Beachwood Dentist
July 15, 2015
 It’s no secret that your body changes when you’re pregnant. Hormones rising and falling, morning sickness, aches and pains, and more can make you feel like your body is out of control. Many patients aren’t aware of how hormonal variation during pregnancy can effect oral health. At the Center for Advanced Dentistry (CFAD), our skilled team will explain the ins and outs of the changes in your oral health while pregnant. If you are pregnant or trying to get pregnant, call to schedule an appointment at our Beachwood, OH office to review oral health and discuss recommended changes to your hygiene routine.
It’s no secret that your body changes when you’re pregnant. Hormones rising and falling, morning sickness, aches and pains, and more can make you feel like your body is out of control. Many patients aren’t aware of how hormonal variation during pregnancy can effect oral health. At the Center for Advanced Dentistry (CFAD), our skilled team will explain the ins and outs of the changes in your oral health while pregnant. If you are pregnant or trying to get pregnant, call to schedule an appointment at our Beachwood, OH office to review oral health and discuss recommended changes to your hygiene routine.
Oral Health Changes While Pregnant
The change in hormone levels puts women at high risk for gum disease, specifically a form of gingivitis referred to as “pregnancy gingivitis.” Thorough at home hygiene and regular six month dental cleaning may not be enough to prevent this form of gingivitis. If you notice inflamed, bleeding or swollen gums, gum sensitivity when eating or drinking, or excessive bleeding when flossing or brushing your teeth, call CFAD immediately. Depending on the severity, we may recommend more frequent cleanings through the course of your pregnancy. Gum disease during pregnancy increases the risk of pre-term birth and underweight babies as well as potentially compromising the baby’s and your immune system if infection enters the blood stream.
Another oral health change noticed while pregnant is the “pregnancy tumor.” The name is quite misleading. A pregnancy tumor is not cancerous. The changes in your body make the mouth’s soft tissue more sensitive to irritation from plaque buildup or foreign debris. These red lumps usually appear on the gums between teeth. If they are extremely painful or impede eating, we may recommend removal, but the tumors typically clear up on their own after you give birth.
Dental Care for Baby from the Dentist Shaker Heights Trusts Most
Did you know your baby’s teeth begin to develop between the 3rd and 6th month of your pregnancy? A healthy diet is essential to a healthy pregnancy, but did you know that eating well can help your baby develop stronger, healthier primary teeth? Your baby needs a lot of vitamins and minerals throughout the pregnancy, but their developing teeth especially need large amounts of Vitamins A, C and D, calcium, protein and phosphorous. Taking a prenatal vitamin as prescribed or recommended by your physician can help you absorb a large percentage of these necessary nutrients, but eating high fiber and protein, and calcium rich foods will provide your baby with more of the necessary nutrients for growth, especially for developing healthy teeth.
Most necessary dental health care is perfectly safe for pregnant and lactating mothers. However, elective procedures should be postponed until after your pregnancy. In the case of dental emergency, more complex restorative procedures may be necessary, but should always be performed in conjunction with your physician.
Contact Your Family Dentist, 44122
At the Center for Advanced Dentistry, we are here to care for you at every stage of your life. If you’re pregnant or trying to become pregnant, call to schedule an appointment to discuss tips for optimal oral hygiene while pregnant. Our Beachwood, OH practice welcomes patients from the surrounding area Shaker Heights, Pepper Pike, Warrensville Heights, Cleveland, and the neighboring communities
Dental Implants As a Gift
November 14, 2012
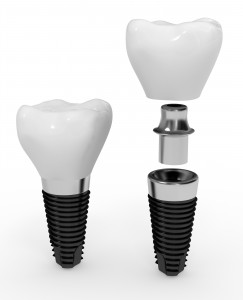 Want to give the gift of dental implants for the new year? It’s not that far fetched.
Want to give the gift of dental implants for the new year? It’s not that far fetched.
You’ve heard a lot about dental implants on this blog for good reason. As a reminder here are some of the reasons why.
- Implants are a safe and organic alternative to other plans
- They can help prevent you from losing more teeth in the future.
- You have the root of your tooth and your smile restored at the same time.
Interested? There are steps to what happens next.
Dr. Hornstein will decide if you or your loved one is a candidate for implants. If Dr. Hornstein believes you are, the proverbial ball can begin rolling as soon as possible. Doesn’t matter if one tooth or a whole row needs replacing, dental implants do the heavy work. By forming an artificial root for your tooth or teeth, these aren’t like dentures. They don’t slip like dentures, so don’t worry about that common problem. You must have a stable jawbone, and if you or your loved one qualifies, get ready for a life-changing experience in only a few visits.
Sometimes, bone grafting may be needed beforehand. Most people qualify for dental implants, so rest assured. Schedule a consultation. In addition to regular brushing and flossing twice a day, regular check-up with Dr. Hornstein will make sure things are going accordingly.
Imagine improved speech along with the confidence found in a bright and healthy smile. Speaking with ease and clarity is always a plus, no matter what your age is. No need for a soft-spoken approach or sentences with only a few words. Dental implants can get you or a loved one on that road.
Give us a call today. The new year will be here sooner than you think. We serve patients from Cleveland, Solon, Shaker Heights, Pepper Pike, and surrounding areas.
Snoring and Sleep Apnea can raise the risk of cancer
May 21, 2012
http://www.foxnews.com/health/2012/05/21/sleep-apnea-can-raise-risk-cancer-studies-indicate/
Sleep Apnea Tied to Increased Cancer Risk
BODY |
By ANAHAD O’CONNOR| May 20, 2012, 5:01 PM
 Ryan Collerd for The New York TimesA CPAP device is used to treat sleep apne
Ryan Collerd for The New York TimesA CPAP device is used to treat sleep apneTwo new studies have found that people with sleep apnea, a common disorder that causes snoring, fatigue and dangerous pauses in breathing at night, have a higher risk of cancer. The new research marks the first time that sleep apnea has been linked to cancer in humans.
About 28 million Americans have some form of sleep apnea, though many cases go undiagnosed. For sleep doctors, the condition is a top concern because it deprives the body of oxygen at night and often coincides with cardiovascular disease, obesity and diabetes.
“This is really big news,” said Dr. Joseph Golish, a professor of sleep medicine with the MetroHealth System in Cleveland who was not involved in the research. “It’s the first time this has been shown, and it looks like a very solid association,” he said.
Dr. Golish, the former chief of sleep medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, said that the cancer link may not prove to be as strong as the well-documented relationship between sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease, “but until disproven, it would be one more reason to get your apnea treated or to get it diagnosed if you think you might have it.”
In one of the new studies, researchers in Spain followed thousands of patients at sleep clinics and found that those with the most severe forms of sleep apnea had a 65 percent greater risk of developing cancer of any kind. The second study, of about 1,500 government workers in Wisconsin, showed that those with the most breathing abnormalities at night had five times the rate of dying from cancer as people without the sleep disorder. Both research teams only looked at cancer diagnoses and outcomes in general, without focusing on any specific type of cancer.
In both studies, being presented in San Francisco this week at an international conference organized by the American Thoracic Society, the researchers ruled out the possibility that the usual risk factors for cancer, like age, smoking, alcohol use, physical activity and weight, could have played a role. The association between cancer and disordered breathing at night remained even after they adjusted these and other variables.
Dr. Mitesh Borad, a cancer researcher and assistant professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic who was not involved with the studies, called the findings “provocative” but said more research was needed to confirm the association. The studies were observational, and other, unknown factors may account for the correlation between sleep apnea and cancer.
Recent animal studies have suggested that sleep apnea might play a role in cancer. When mice with tumors were placed in low-oxygen environments that simulate the effects of sleep apnea, their cancers progressed more rapidly. Scientist speculate that depriving mice of oxygen may cause their bodies to develop more blood vessels to compensate, an effect that could act as a kind of fertilizer for cancer tissue and cause tumors to grow and spread more quickly.
The researchers wondered whether a similar relationship might exist in people with sleep apnea, in whom throat muscles collapse during sleep, choking off the airway and causing gasping and snoring as the body fights for air. Severe sleep apnea can produce hundreds of such episodes each night, depleting the body of oxygen.
In one study, a team at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health examined data on state workers taking part in the long-running Wisconsin Sleep Cohort, who since 1989 have undergone extensive overnight sleep studies and other measures of health about every four years. The landmark project was one of the first to reveal the widespread occurrence of sleep apnea in the general population.
The researchers found that the more severe a person’s breathing problems at night, the greater the likelihood of dying from cancer. People with moderate apnea were found to die of cancer at a rate double that of people without disordered breathing at night, while those in the severe category died at a rate 4.8 times that of those without the sleep disorder.
“That is really striking,” said Dr. F. Javier Nieto, one of the study’s authors and chairman of the department of population health sciences at the University of Wisconsin. “It could be something else, but it’s hard to imagine that something we didn’t control for is causing this.”
In the second study, researchers with the Spanish Sleep Network took a slightly different approach, looking not at cancer mortality among apnea patients, but at the incidence of cancer. They used a measure called the hypoxemia index, which looks at the amount of time the level of oxygen in a person’s blood drops below 90 percent at night.
About 5,200 people were followed for seven years, none of whom had a cancer diagnosis when the study began. The researchers found that the greater the extent of hypoxemia, or oxygen depletion, during sleep, the more likely a person would receive a cancer diagnosis during the study period.
People whose oxygen levels dropped below 90 percent for up to 12 percent of the total time they were asleep, for example, had a 68 percent greater likelihood of developing cancer than people whose oxygen levels did not plummet at night, said study author Dr. Miguel Angel Martinez-Garcia of La Fe University and Polytechnic Hospital in Spain. As time spent without oxygen increased, so, too, did cancer risk.
Although the study did not look for it, Dr. Martinez-Garcia speculated that treatments for sleep apnea like continuous positive airway pressure, or CPAP, which keeps the airways open at night, might reduce the association.
The Wisconsin study also did not specifically look at the impact of treatment for apnea on survival, either, but when people who were being treated with CPAP were removed from the analysis, the cancer association became stronger, “which is consistent with the hypoxemia theory,” Dr. Nieto said.
“I would say that this is one more instance that shows that sleep apnea can have profound impacts for people’s health,” he added. “Not breathing while you’re sleeping is a serious problem.”
Want a New Smile for the New Year? Try Invisalign from The Center for Advanced Dentistry!
December 22, 2011
 As the new year approaches, are you considering ways to improve your life…and your smile? At the first of every new year, people make resolutions to get in shape, get more organized, and update their looks. If you’ve struggled with crooked teeth for a while, you know what damage it can do to your self-esteem, but there’s a fairly easy and painless way to change all of that with Invisalign clear aligners from Drs. Hornstein and Gray at The Center for Advanced Dentistry in Beachwood.
As the new year approaches, are you considering ways to improve your life…and your smile? At the first of every new year, people make resolutions to get in shape, get more organized, and update their looks. If you’ve struggled with crooked teeth for a while, you know what damage it can do to your self-esteem, but there’s a fairly easy and painless way to change all of that with Invisalign clear aligners from Drs. Hornstein and Gray at The Center for Advanced Dentistry in Beachwood.
Our dentists consider themselves smile artists. They can fit you for Invisalign clear braces, which will slowly move your teeth into a straighter position without the hassle, discomfort, and unattractive look of traditional orthodontics.
Why choose Invisalign clear braces for your smile makeover from The Center for Advanced Dentistry?
- Comfort: Traditional braces can irritate soft tissues in the mouth. Invisalign aligners are smooth, making for greater comfort.
- Ease of hygiene: To clean your teeth and braces, you simply remove your aligner, allowing you to brush and floss normally as well as clean your orthodontic appliance.
- Attractive: Because they’re clear, people will hardly notice your Invisalign aligners, and if you need to remove them to look your best for a big event, you have the freedom to do so!
Don’t let another year pass without getting the beautiful smile you deserve. Contact The Center for Advanced Dentistry in Beachwood today to discuss Invisalign clear orthodontics!
Smile Makeover, Part 3: Put Your Best Smile Forward with Porcelain Veneers or Lumineers
November 10, 2011
 In our post from October 14th, we talked briefly about Invisalign clear braces and how they can help patients in search of a smile makeover find exactly what they’re looking for—a straight, confident smile.
In our post from October 14th, we talked briefly about Invisalign clear braces and how they can help patients in search of a smile makeover find exactly what they’re looking for—a straight, confident smile.
But not every patient wants, or needs, to commit to an orthodontic solution like Invisalign. That’s why Dr. Hornstein’s Beachwood office also offers porcelain veneers and Lumineers. Both are popular cosmetic solutions that can help patients hide cracked, chipped, or slightly misaligned teeth, in addition to stains teeth whitening hasn’t been able to erase.
Give Your Smile an Extra Level of Protection with Dental Sealants
August 26, 2011
 When food particles and bacteria find their way into the pits and grooves in your teeth, tooth decay is the result. That’s why brushing and flossing are so important. By maintaining a regular brushing and flossing routine, you’re giving your smile the protection it needs to stay strong and healthy.
When food particles and bacteria find their way into the pits and grooves in your teeth, tooth decay is the result. That’s why brushing and flossing are so important. By maintaining a regular brushing and flossing routine, you’re giving your smile the protection it needs to stay strong and healthy.
But even the best brushers need a little help sometimes. That’s why, at Dr. Hornstein’s Beachwood office, we offer dental sealants. Dental sealants let us give your smile that extra little bit of protection it needs in areas that may be harder to protect.
What are Dental Sealants and How Do They Work?
Dental sealants are applied directly to your teeth after they’ve been cleaned and dried. Then, they’re hardened with a curing light, turning them from a liquid into a thin plastic film. This thin film acts like a barrier for food particles, keeping them away from vulnerable parts of your smile and helping you maintain your optimal oral health.
What’s more, dental sealants can be applied in very little time—anywhere from 10 to 45 minutes, depending on how many teeth Dr. Hornstein will be sealing.
If you’d like to know more about dental sealants, contact our Beachwood dental office to schedule an appointment with Dr. Hornstein. We serve patients from Cleveland, Solon, Shaker Heights, Pepper Pike, and surrounding areas.

 That your mouth is the main gateway to the rest of your body should come as no surprise. Every day the food and nutrients your body needs enter through your mouth. If you need medication, then in most cases that medicine is swallowed and helps you via your digestive system. And sadly, even things that may not be so healthy for the body also enter through the mouth, such as tobacco and alcohol to excess.
That your mouth is the main gateway to the rest of your body should come as no surprise. Every day the food and nutrients your body needs enter through your mouth. If you need medication, then in most cases that medicine is swallowed and helps you via your digestive system. And sadly, even things that may not be so healthy for the body also enter through the mouth, such as tobacco and alcohol to excess.